
Getting Started in Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Buyer Personas
While buyer personas may not sound like they pertain to non-profits because you aren’t selling anything, they are just as important to you as they are to a for-profit business. In the case of non-profits, they could technically be called donor personas, but the same rules apply.
If you don’t know who your target market is, you don’t know what keywords they will be searching for. Buyer personas are fictional buyers based on the characteristics of your current or ideal clients. These personas should include more than just buying habits, they should also take into account demographics, behaviors, and pain points.
Getting into Your Clients’ Heads
The biggest mistake companies make in SEO is thinking like themselves instead of like their customers. If you approach SEO as an employee or company owner, you will most likely never come up with the keywords your prospects are using in their searches. You need to use your buyer personas to determine who your target audience is, think like them, look at your non-profit through their eyes, and use the terms they would use instead of industry jargon.
For example, say you were a used car salesperson in Charleston. You have learned to say “pre-owned vehicles” instead of “used cars,” and you use this phrase when talking to customers. But will your prospects be searching for “pre-owned vehicles”? No, they will be searching for “best used cars in Charleston,” and your keywords need to reflect that.
Intent
SEO used to be all about keywords, so businesses stuffed as many keywords as possible into their content. Today, Google is constantly attempting to figure out what searchers hope to find, so it is using other data, like long tail keywords and location information, to provide search results.
When you are doing SEO, you should not only make sure you are keeping in mind what people are trying to accomplish with their searches, you should also help Google understand the intention of each page of your website. To accomplish this, don’t put more than one topic on a page, and have clear titles. For example, a page about your founder should only introduce him or her to the reader, not also try to provide unrelated information.
Keyword Research
When doing keyword research you should consider three important questions:
- What terms do I want to rank for?
- How realistic is it that I will rank for these terms?
- What is the intent of the searcher?
Of course you want to rank high for the terms everyone searches for when it comes to non-profits, but keep in mind the keywords with the most searches per day are also the most competitive. You need to find terms with a good balance of searches and competitiveness, so terms that get enough searches to drive traffic to your site, but low enough competition that you can rank for the term in a reasonable amount of time. As far as the intent of the searcher, don’t use keywords with several different meanings because it won’t be clear to Google what you want searchers to know about you.
SEO Tools
The following are three free SEO tools that are easy to use.
Google Search
Open Google and begin typing a possible keyword in the search bar. Look at what Google fills in as it tries to determine what you might be trying to find. These suggestions are based on what people are searching for and what Google thinks your intent is. If they apply to your organization and the information you want searchers to find, use these words and phrases as your keywords.
Google Keyword Planner
To use this tool, you will need to set up a Google Adwords account (you don’t have to run or pay for ads to use the tool). To set up an account and use this tool:
- Open Google with the email you want connected to the Adwords account.
- In a separate tab, google “Google Keyword Planner” and follow the directions to set up the account.
- Enter your potential keywords and Google will give you related terms and data on whether or not they are terms you are likely to rank for (volume, cost per click, competition). Use this data to decide which terms will be the most effective.
Ubersuggest
Neil Patel, a well-known digital marketer, is currently offering this tool for free to drive traffic to his site. You can use it to check the effectiveness of your current site by inputting your own domain name and reviewing the results.
To use it as a keyword tool, input a successful competitor’s domain to see what keywords they are ranking for, then use them on your site. It will also show you which of their pages are performing well, so you can compare their content and design to your own.
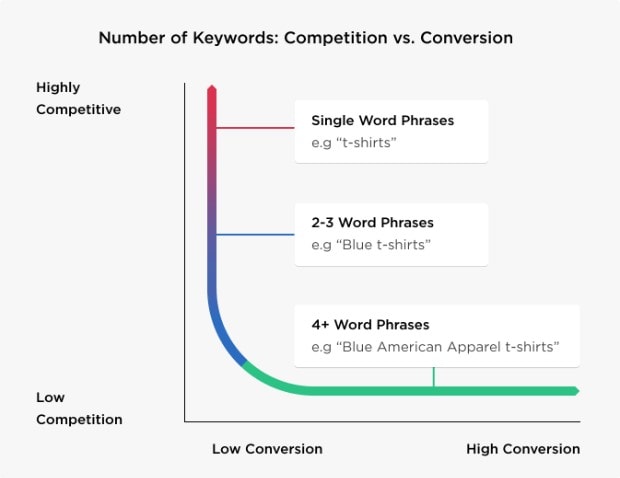
Long Tail Keywords
Long tail keywords are made up of several words instead of just being one or two words. They are much easier to rank for because they are more specific, and searchers who use them are more likely to convert because they are focused on what they want and know you offer it. Successful conversion can mean they call you, fill out a form with their contact information or make an actual purchase (or in the case of a non-profit, make a donation).
This graph illustrates that the shorter the keyword, the higher the competition, and that as you add words, the competition lessens and the conversion rate increases.
Meta Tags
Meta tags aren’t as important as they used to be, but they are still a useful SEO tool. The most critical meta tags are the meta title and meta description. The best practices for meta tags are:
- Keep meta titles at 60 characters or less
- Don’t overuse keywords
- Give every page a unique title
- Put the most important keywords first
- Take advantage of your brand (put your name in the tag)
- Write for your target audience
Meta Title
A meta title specifies the title of the webpage and appears on the search engine results page (SERP) as the clickable title that takes the viewer to the page. It can include keywords, but should still be an accurate description of what the viewer will find on the page.
Not all characters take the same amount of room, so 60 characters may be shorter or longer depending on what letters or symbols are used. Moz provides an SEO title tag preview tool that shows exactly what your title will look like. This is useful because you want to show the maximum amount of information possible while still staying within the viewable space.
The meta title also shows up in the tab at the top of your internet browser window when you open a page and in your post when you share a link on social media.
Meta Description
The meta description summarizes the content on a page and tells the search engine and your readers what the page is about. Just like the meta title, it can include keywords, but only if they truly pertain to the content on the page and aren’t overused. It should be as close to 155 characters as possible.
Adding meta tags is quite easy in WordPress. We recommend the Yoast plug-in for this task because it is user-friendly and doesn’t require the use of any code. Yoast will automatically populate the meta title and description for each webpage, but you can edit both to be more accurate. This plug-in also shows you when you have reached the optimal length of both fields.
Optimizing Text on the Website for SEO
The best rule of thumb to follow when optimizing text on your website is to remember you are writing for people, not robots.
Use your primary keyword in your headline, also known as the H1 tag. Other than the meta tags, this is the most effective way to optimize the content on your page.
Aim for .5 to 2.5 percent of keywords in your copy, just enough for Google to know what your talking about.
Use both primary and related keywords in your content. Google can now understand natural language and how we speak, so you can include synonyms in your text without confusing the search engine.
Include plenty of context. There needs to be enough content around the keywords so your readers, and Google, aren’t confused and can understand what your content means.
Blogging
You need a blog. If you think people don’t read anymore, you are wrong. Video is extremely important to your website, but people are asking questions and Google still understands words better than video. Your blogs should answer all of the questions people are asking.
Fresh Content
A blog keeps your website fresh and current, which means Google keeps indexing your site and will continue to offer your site to searchers over other sites with outdated content. Unless you are constantly updating the content on your regular pages, which is unlikely, blogging is the only thing refreshing your content.
Longer Visits
A blog also keeps people on your website longer. Bouncing means a visitor quickly leaves because they didn’t find what they had hoped to on your site. Google will stop ranking your site for that term if people continue to bounce. A blog will keep them on your site longer and help them discover other pages and information on your site.
A Good Place for Long Tail Keywords
Long tail keywords can often be more easily targeted in blogs than on other webpages because you can continue to write blog posts about them. This convinces Google even more that you have the answers to the questions people are asking. A blog is also a perfect place to use internal links, which lead your visitors to other pages on your site and helps Google determine your most important pages.
Encourages Backlinks
A blog gives other websites more reasons to link back to your site. For example, say you have a blog post about how to choose the right non-profit and you are getting a lot of traffic to it. You can then go to other websites and ask if they would be interested in linking to it. If they do, it provides a backlink to your site, which increases your standing with Google.
Builds Stronger Relationship
Blogs help you connect with your audience. You can offer more personalized content with a blog than you can on other pages of your site because the number of posts you write is unlimited, unlike regular webpages.
Linking
Internal links between pages and blog posts tell Google which pages are most important and what your website is all about. They also keep visitors on your site longer, because they can follow the links to other pages on your site and continue reading.
Backlinks
A backlink is when another website links back to yours. This is the most important type of link because it shows Google that another website owner finds your content valuable enough to link to it. The more credible and relevant the website linking to yours is, the better the backlink.
Unfortunately, backlinks can be difficult to obtain, but here are some of the best options:
- Guest blog for larger sites. Everyone needs great content, so offer to write a blog for another website in exchange for a backlink.
- Offer your content as a resource. If you have an ebook or other piece of content that others will find valuable, tell them they can link to it as a resource for their readers.
- Submit an article to HARO (Help a Reporter Out) or answer questions on other sites. This not only provides a backlink, it also helps your brand by showing you’re an expert in your field.
- Get listed in directories. This is one of the easier ways to get backlinks, but it needs to be done right. Only ask to be listed in credible directories that are relevant to your organization, don’t ever pay money to be listed in thousands of random, and usually fake, directories just for backlinks. Google knows the difference and may penalize you for it.
What Is the Second Largest Search Engine?
Believe it or not, after Google, YouTube is the largest search engine, which means creating and posting video on this platform is a critical part of any marketing strategy.
Optimizing YouTube Videos
Optimizing videos on YouTube is very similar to optimizing the content on your website.
- Make sure the video file name has a keyword.
- Make sure the video title has a keyword.
- Optimize the video’s description so it includes keywords and tells what the video is about.
- Tag relevant keywords to make the video easier for searchers to find.
Treat each video like a separate piece of content and make sure your cover page is professional looking and uses the proper image size, which is quite large.
Optimizing Video Thumbnails
Thumbnails are what appear when someone does a search on YouTube. They also appear along the side of the screen as suggestions when someone is watching a video. Making your thumbnails look their best will encourage viewers to click and watch.
- Each thumbnail should use the right size image so it doesn’t look pixelated or shrunk
- Use a clear, high-resolution photo
- Include title text, even in the image, so viewers know what the video is about and to help SEO.
- Use fonts consistent with the rest of your branding
- Create a branded template so viewers easily recognize your videos
- Use contrast in your design to make the image stand out
- Be honest and accurate about what the video is about in the title and description
- Use software like Canva to help make your thumbnail design look professional
The Future of SEO
Voice is the future of SEO. It’s projected that by 2020, 50% of all searches will be voice searches, so start taking steps now to help your website be found in voice.
Using structured data gives Google a little extra information about your webpage and helps with voice search. If you don’t have WordPress, you might be better off having a professional to do this, If you do use WordPress, it is not too challenging to do with the right plug-in. Claiming your Google My Business listing and controlling the information in it as much as possible, is also beneficial.
What to Do After the Basics
Continue to measure your SEO success and adapt as necessary. Use Google Analytics and Ubersuggest SEO Analyzer to see where you are now, then create a plan to increase the effectiveness of your SEO efforts.
Links to Resources
Digital Marketer Avatar Worksheet
The Importance of Intent in SEO - Search Engine Land
Types of Meta Tags Explained - Word Stream
Adding Meta Descriptions to Your Site using Yoast
How to Optimize Text on Your Website
Common Model for Internal Linking
How to Optimize Videos on YouTube for SEO